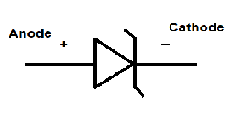Schottky diodes
Schottky diodes,metal/semiconductor junction: this heterogeneous junction is characterized by the absence of storage of charges, it is therefore very fast. It is widely used in circuits fast logic (TTL Schottky). Schottky diode symbol A schottky diode works exactly the same as a diode.The differences are: At the threshold voltage, which is no longer 0.7V, but 0.3V, at 0.4V In terms of speed, schottky diodes are much faster and more expensive Application: Logic circuits: TTL LS technology and derivatives Switching power supply POWER SCHOTTKY DIODES: reduction of the voltage drop in the on state (0.4V at 1A/mm²). no reverse recovery phenomenon (therefore very fast diode) but appearance of a negative current of the same order of magnitude as the current of the fastest diodes. only limitation: Reverse voltage withstand. it is difficult to exceed 200V Varactor diode This reverse biased diode behaves like a very low value capacitor, the capacity of which...